The noun is a part of speech in the English Language, which characterizes the name of anything you want to write.
What is a Noun?
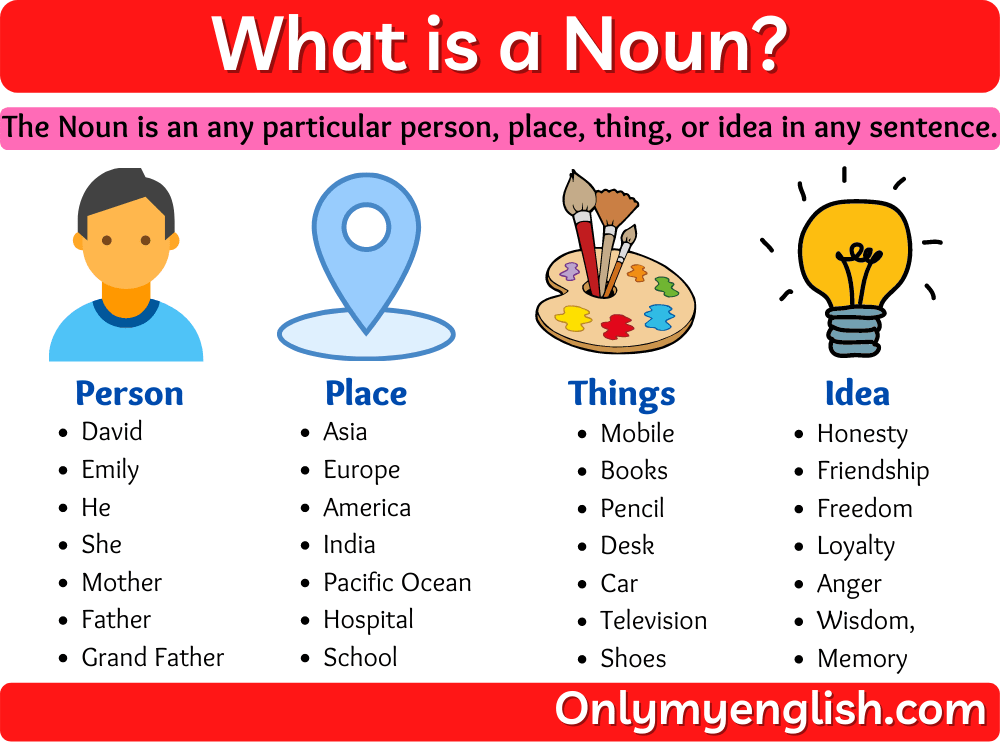
The Noun which describes the name of any particular person, place, thing, or idea in any sentence.
Most of the time, in a sentence, the subject is also a noun of anything. It can be the name of a specific or some general place, person, thing, object, or idea.
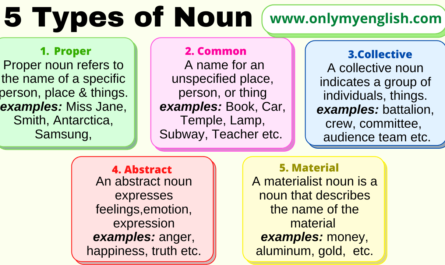
Depending on that, Nouns is classified into several types, like Common, Proper, Abstract, Collective, and Material noun.
A noun is one of those parts of speech in the English language, which is very easy to understand and identify from any sentence. Most of the nouns are real and also conceptual, so that it may come in different types of the noun.
The nouns like a place, person, things, objects, are called Concrete nouns, and the noun which comes from different concepts, like emotions, ideas are called Abstract nouns.
Types of Nouns
According to the name of any particular person, place, thing, or any idea in a sentence,
The noun is classified into twelve different types
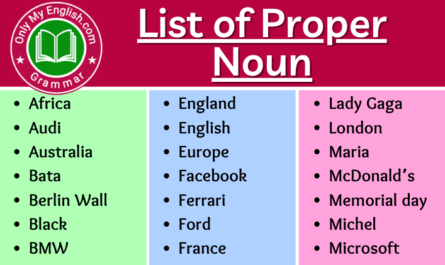
- Proper Noun
- Common Noun
- Concrete Noun
- Abstract Noun
- Countable Noun
- Uncountable Noun
- Compound Noun
- Collective Noun
- Singular Noun
- Plural Noun
- Possessive Noun
- Material Noun
Examples of Noun
- Proper Noun: David, Asia, Sun, Mount Everest, Pacific Ocean
- Common Noun: Men, Country, Mountain, Ocean, Book
- Concrete Noun: Ship, Town, Table, Vehicle, Whale, Wings
- Abstract Noun: Ability, Calm, Death, Faith, Joy, Skill, Sacrifice
- Countable Noun: Apple, Peanuts, Money, Orange, Mouse
- Uncountable Noun: Salt, Sand, Sugar, Water, Meat, Coffie
- Compound Noun: Airport, Classroom, Eardrum, Doorway
- Collective Noun: Colony, Batch, Choir, Organization
- Singular Noun: Bird, Pen, Shirt, Army, Fork, Candy
- Plural Noun: Birds, Pens, Shirt, Armies, Forks, Candies
- Possessive Noun: Dog’s, Children’s, Jame’s
- Material Noun: Iron, Coal, Water, Sugar, Oil, Glass
Countable nouns:
Countable nouns are those nouns that can easily be counted.
The majority of the nouns can be categorized in the countable noun list, which includes people, things, animals, or objects which can easily be counted.
For some nouns which are unique and also singular, they prefer at the beginning.
Examples:
- The spider has eight legs.
- Put all the five bottles of Cold drinks in the refrigerator.
- His brother purchased a car from the showroom this morning.
Uncountable nouns:
Uncountable nouns are those nouns that are uncountable or cannot be counted easily.
These nouns are also called Mass nouns.
In certain things like milk, salt, water, rice, sun rays, etc. that are uncountable in numbers are called uncountable nouns.
To count such things, we use some words along with it like, a full glass of milk, a cup filled with sugar, a water bottle, a sack of rice, a packet of salt, etc. because these things cannot be counted, can be measured in specific quantities.
Uncountable nouns do not have any singular or plural forms.
Examples:
- The swimming pool has plenty of water this time.
- Put some extra cheese on my pizza.
- Let’s get rid of this critical situation.
Masculine and feminine nouns:
Masculine nouns are the nouns of the male gender, including persons, animals.
For example,
- King, boy, man, cock, horse, lion, tiger, dog, etc. are masculine nouns.
Feminine nouns are such nouns include females include persons, animals.
For example:
Queen, girl, women, hen, duck, tigress, etc. are feminine nouns.
Singular and Plural nouns:
The nouns that can be categorized by the numbers are called Singular nouns and Plural nouns.
Singular nouns have a single number/quantity of person, place, thing, or one idea.
For example,
- Boy, car, man, beach, etc. are singular nouns.
A plural noun is a word representing more than one person, place, thing, or idea.
The plural noun comes in a sentence where we have to represent more than one quantity of anything. For that, we don’t have to add any other word in a sentence, just adding “s or es” on that particular word, which is going to be plural.
For example,
- Boys, girls, dogs, animals, beaches, etc. are plural nouns.
Let us see some examples from each type that explain the noun functions as a subject in a sentence.
- James ate his friend’s lunch box in the school. (Concrete noun- person, place, object)
Here, “James” is the name of a person and a subject followed by the verb “ate”.
In this example, two more nouns are present: “lunch box” and “school” and the article “the” represents a specific school where James is studying.
- Let me introduce you to Mr. Jack Fernandez, the CEO of our company. (Concrete noun- person, place)
Here, the subject is indirectly present in the sentence, and “Mr. Jack Fernandez” is the noun and another noun is “CEO” which is represented by “the” article for a particular company.
- He is studying with full concentration during exams. (Abstract noun-emotion)
Here, concentration is an abstract noun that represents the emotional feeling.
- Samuel and his colleague both were gone to the library to get a book related to their project purpose. (Concrete noun- person, place, thing)
Here, “Samuel” is a subject and a proper noun, the name of a person. The word “colleague, library, project, and a book” are also nouns of different types.
- He went to Malaysia for a tour. (Concrete noun- place, Abstract noun- idea)
Here, Malaysia is a proper noun representing a place, and “a tour” is an idea.
- I feel very bad for him, depending on which situation he is passing by. (Abstract noun- emotion)
Here, bad is a noun to express a feeling.