The pronoun can be defined as, “A pronoun is one of the parts of speech, is a word that comes in a sentence as an alternative to the noun.” Also, we can say, a pronoun is a replacement for a noun or a noun phrase in a sentence.
What is a Pronoun?
When we have to introduce any person in a sentence more than once, then repetition of the same name in a single sentence looks unusual, that time we replace all other nouns with a pronoun.
Pronouns are short words and function the same as that the noun does in a sentence.
It may be functioning at any place in a sentence like the first person, second person, or third person, respectively.
It can function as a subject, object (direct/indirect), place, animal, thing, etc.
Some common pronouns used most commonly in a sentence are- He, She, It, They, We, Us, I, You, Them, anyone, Something, Nobody, etc.
Usage:
The naming word for representing any male person, and for first, second or third person, we use “He, his, him, himself” as a pronoun,
For example,
- James, Jonathan, Robert, Andrew, David, Dwane Johnson, etc. – He, his, him, himself respectively.
Similarly, for representing the naming word for a female person, and for the first, second, or third person, the “She, her, hers, herself” pronoun is used in a sentence.
For example,
- Sara, Stephney, Lisa, Malina, Agatha, Martha, Julia, Abella, Senorita, etc. – She, her, hers, herself respectively.
And for representing any objects or things like tea, coffee, box, chair, shoes, etc. – the pronoun “It, itself” is used in a sentence or a phrase or a clause.
For Plural words or common from gender, more number of persons, places, objects, first and third person, etc. pronouns like I, you, us, we, they, them, their, theirs, themself, themselves, etc. can be used in a sentence.
Examples:
Let us see the replacement of noun with the pronoun in the below example to understand clearly,
- Andrew goes to school every morning with Andrew’s bicycle.
Andrew goes to school every morning with his bicycle.
He goes there every morning with his bicycle.
Here, in the above sentences, the noun Andrew (person)is replaced with “he”, and the school (place) replaced with “there”, and Andrew’s replaced with “his”.
- Clara, Jordan, and Elle are playing a carrom game together.
They are playing a carrom game together.
- Is Robin coming to the party with Nora?
Is he coming there with her?
Types of pronoun:
There are eight sub types of pronoun,
- Personal pronoun
- Possessive pronoun
- Reflexive / Intensive pronoun
- Reciprocal pronoun
- Demonstrative pronoun
- Indefinite pronoun
- Relative pronoun
- Interrogative pronoun.
Let us see some short description of each subtype of the pronoun:
Personal pronoun:
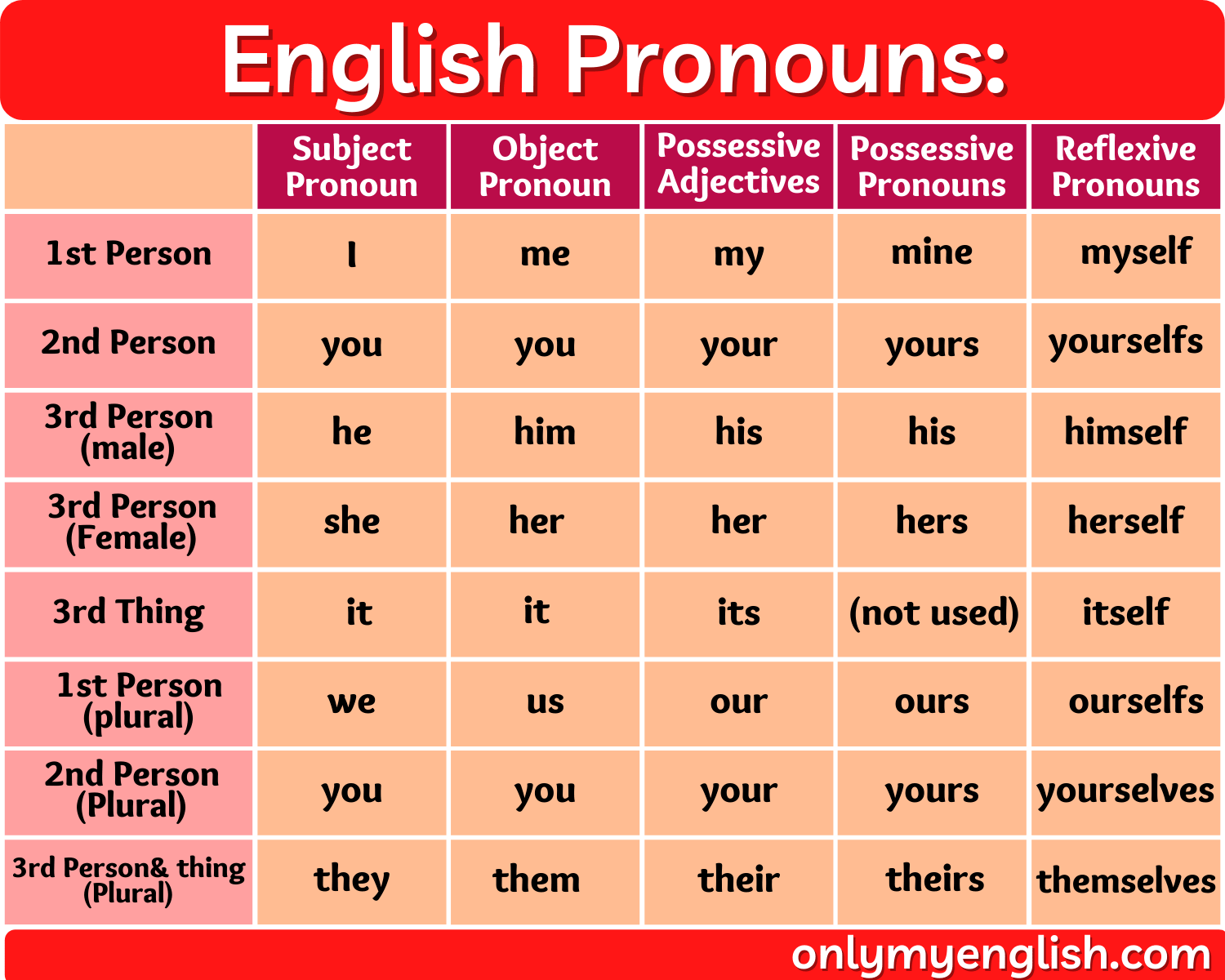
Personal pronouns have various forms with respect to numbers (maybe in singular or plural), gender, things, person, animals, or formality.
In any sentence, if the personal pronoun and the subject of the sentence (maybe a person, place, thing, object) both are the same, then the pronoun is also called the Subject pronoun too.
- I, we, him, you, she, he, it, they, me, her, us, and them are all personal pronouns.
- For the person: represents a speaker in the sentence. (first-person “I”, second person “You”, or third person “He, She, It”).
- For the gender: represents the gender of the speaker in a sentence. (masculine or feminine or any object called neuter).
- For the number: represents the quantity or number of object, person (singular or plural).
Examples:
- He needs to start upgrading himself.
Here, he is a subject pronoun as well as a personal pronoun.
- They have decorated the entire function within 2 hours.
- I want you to come and play with us.
- Somebody go and call them to come immediately and report on the ground.
Possessive pronouns:
The pronoun, which shows some relation or possession quality or direct relation with someone else, is called a possessive pronoun.
- mine, ours, yours, his, hers, its, theirs, etc. are possessive pronouns.
If it comes to a place of the person with respect to the singular and plural form.
Say the first person: Singular- My, mine.
Plural- Our, ours.
For the second person: Your, yours.
For third person: Singular- His, hers, it’s.
Plural- Their, theirs, Whose.
Examples,
- We had spent a lot of time with Jimmy and his sister.
Here, “His” is possessed for a person Jimmy in a sentence.
- This is my personal matter. You better stay out of it.
- This sports-car is mine.
- Hey dude! What is your problem?
Reflexive pronoun:
The reflexive pronoun is a word that is identical to a pronoun or a reflection of a noun, pronoun, adjective, or adverb that reflects back to the subject in a sentence. These pronouns can be ended by the suffix ‘-self’ or ‘-selves’.
The intensive pronoun (also called emphatic pronoun) is the same as that of the reflexive pronoun, but it is used for other nouns or a pronoun present in a sentence to indicate that noun or pronoun separately.
- Ourselves (self), yourselves (self), themselves(self), myself, herself, himself, itself, etc. are reflexive pronouns.
For the first person: Singular- Myself.
Plural- Ourselves.
For the second person: Yourself, Yourselves.
For the third person: Singular- Himself, Herself, Itself/Oneself.
Plural- Themself/Themselves.
Examples,
- He slapped himself in front of others.
Here, the reflexive pronoun “himself” introduces the speaker “He”.
- Do not blame themselves for this huge loss.
- I took myself inside the museum.
- We don’t have to go to the party, we can enjoy ourselves.
Reciprocal pronoun:
The reciprocal pronoun is used when there is more than one subject acting in the same way
towards each other.
- To one another (when referred to more than two people).
- To each other (when we refer two people).
Examples,
- Cadets are wishing one another for their better future life at their farewell.
Here, the number of cadets is not mentioned in the sentence, and the reciprocal pronoun one another is used to represent all.
- Seetha and Geetha caught talking to each other during the examination.
- The kidnappers are blaming one another after their failure.
- Both are like best friends, always supporting each other.
Demonstrative pronoun:
The pronoun which is used to demonstrate something specific or to improve nouns and pronouns in any sentence. This pronoun can be either singular or plural also, it can be used in place of a noun.
- This, that, these, those, etc. are demonstrative pronouns.
Examples,
- You have never imagined this in your life.
Here, this refers to any incident that happened in life.
- That bike looks like a Harley Davidson.
- Can you share those pictures which we clicked last evening?
- Each of these pictures is looking so funny.
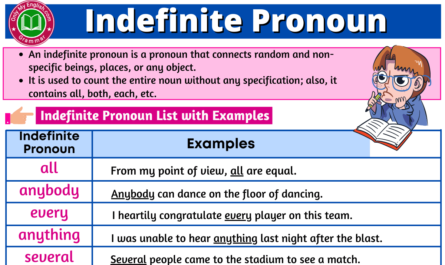
Indefinite pronoun:
Indefinite pronouns are used to mention one or more unidentified objects, places, or persons because they do not specify any precise object, place or person.
- Any, other, either, nobody, some, someone, somebody, something, anyone, everything, all, both, several, much, whoever, whichever, anybody, nothing, none, no one, etc. are indefinite pronouns.
Examples,
- All of you belong to the same place.
Here, all is representing a proper noun.
- Somebody is absent in today’s class.
- Nobody comes forward to save that woman who was caught in the road accident.
- Either you answer my question and sit or get out of the classroom.
Relative pronoun:
A relative pronoun is a pronoun which is used to express the relation between corresponding persons, places, things in a phrase or a clause of any sentence.
This pronoun can also operate as a possessive pronoun, which is useful in connecting two sentences.
- Whoever, whom, that, who, which, whose, what, where, when, etc. are relative pronouns.
Examples,
- The bird which is sitting on a branch of that tree looks very big in size.
Here, the relative pronoun “which” relates a bird with a clause of the sentence.
- The athlete who won the gold medal in the Olympics was trained hard.
- The chicken grills that she baked yesterday on the barbecue were so delicious.
- The selected players, whoever the committee selects, will report tomorrow morning on the ground.
Interrogative pronoun:
An interrogative pronoun is a pronoun that means to interrogate or to ask questions easily. It can also be used as relative pronouns sometimes or to ask an indirect question.
Most of the time, this pronoun comes at the starting point of the sentence.
- Who, whose, what, which, and whom, etc. are interrogative pronouns.
Examples,
- Who is going to tell a story?
Here the answer is the noun of the sentence and is asked by “who”.
- Whose Pendrive had lost yesterday?
- What are you expecting from me?
- Which people come from a powerful place?
- You do not have any idea to whom you are talking?
In certain situations, rarely used interrogative pronouns end with a suffix- ever, and -soever.
- Whoever, whomsoever, whatever, etc.
For example,
- Don’t harm any hostages; whatever you want, the government will provide you.