Definition
In the English Language, a phrase is simply a union of two or more than two words that also functions as a noun, that does not have any finite verb or a subject.
It does not contain any clause elements like subject, verb, and object of a preposition and a noun, pronoun, verb, or adverb.
What is a Phrase?
Phrases can act as a part of speech as the words of a phrase act together as a single grammatical unit to function in a sentence, but it does not stand alone as a sentence.
The length of the phrase can be at least two words. It combines to make some clauses and sentences.
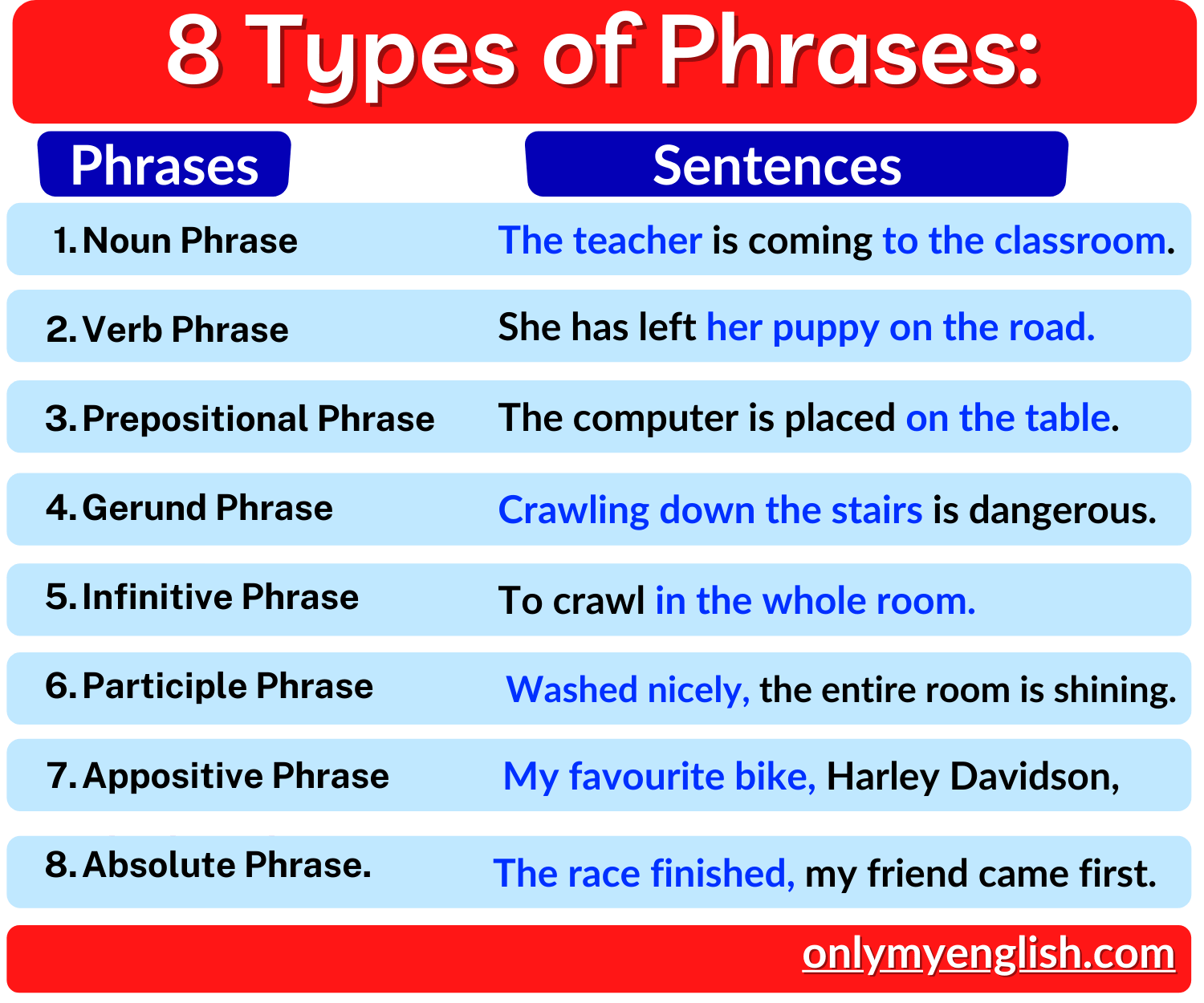
Types of Phrases:
Generally, there are eight types of phrases,
- Noun Phrase
- Verb Phrase
- Prepositional Phrase
- Gerund Phrase
- Infinitive Phrase
- Participle Phrase
- Appositive Phrase and
- Absolute Phrase.
Out of which there are three types of Verbal Phrases:
- Gerund Phrase
- Infinitive Phrase and
- Participle Phrase.
Noun Phrase:
A phrase is called a noun phrase where it consists of a noun (head noun) or a pronoun along with its modifiers.
Nouns like people, places, things, animals, or ideas come in a sentence with a single modifier or more modifiers.
We can understand by the help of examples,
- The teacher is coming to the classroom.
- Here, “the teacher” and “to the classroom” are noun phrases, where “the” and “to the” are modifiers, and “teacher” and “classroom” are head nouns respectively.
- This was a movie as old as time.
- Her husband is a public servant.
- Split some water on the flowerpots.
- I always wanted to buy a car.
Verb Phrase:
A verb phrase is a combination of verbs (main verb and helping verbs) that may be in numbers that are together working in a sentence.
It also contains its modifiers and adverbs, which are used to change the meaning of the verb phrase.
Examples:
- Was running behind.
- Has caught.
- Had gone.
- Will have forgotten.
Examples of verb phrases with the sentence:
- We had not played any games since yesterday.
Here, “had not played” is a verb phrase where “had” is a modifier and “played” is the main verb.
- The car is blowing away very far away in the tornado.
- She has left her puppy on the road.
- The cloth will have been flying high in the sky.
- I have been coming to your wedding anniversary.
Prepositional Phrase:
The prepositional phrase is a combination of words that contain words like a preposition; the rest part called the object of a sentence includes a noun or a pronoun.
This phrase begins with a prepositional word, and the word can also perform functions like a noun, adjective, or adverb respectively.
An adjective can also be used in between the preposition and the object in prepositional phrases and then it modifies a noun or a pronoun of a sentence.
Examples:
- The computer is placed on the table.
- Here, “on the table” is a prepositional phrase that starts with a prepositional word “on”, and rest is the object of a sentence.
- We are about to reach our destination.
- The man is running against the train.
- The train was left before its time
- He is swimming below the surface.
Gerund Phrase:
The gerund phrase is a type of verbal phrase or a noun phrase that begins with a gerund (functions as a noun).
It contains a gerund, modifiers, and the object of a sentence.
Simply, we can say that a gerund is a verbal word that ends with -ing (the present participle), and acts as a subject, object, a noun, or a complement too in a sentence.
Examples:
- Crawling down the stairs is dangerous.
- Here, “Crawling down the stairs” is a gerund phrase where, “crawling” is a gerund that functions as a noun, and “down the stairs” is an object.
- Shining of the sun is like a pearl up from the ocean.
- Falling from the bicycle makes him injured.
- Unboxing the gift wrapper quickly without damaging it is also an art.
- Playing cards on the train is a real fun while travelling.
Infinitive Phrase:
An infinitive phrase is a phrase of the noun which starts with an infinitive verb and also consist
Modifiers.
An infinitive phrase is a type of verbal phrase.
Examples:
- To crawl in the whole room.
- Here, “to crawl” is an infinitive verb in an infinitive phrase and rest is a modifier or an object.
- To work in the middle of something.
- To donate some charity is a good thing. (subject)
- They have decided to go for a long drive at night. (direct object)
- She took leave to complete her assignments at home.
Participle Phrase:
A participle phrase is a type of verbal phrase that begins with a verb and that verb is either in past participle form or in a present participle form along with a modifier.
Examples:
- Traveling on the bus.
- Something is fishy.
- Stood on a chair.
Examples of Participle phrases with the sentence:
- Washed nicely, the entire room is shining.
- Here, “washed nicely” is a participle phrase where washed is a participle in past participle form and nicely is a modifier.
- The frog, hidden over all summer, finally came up in the rainy season.
- We keep moving forward till we reach our destination.
- Around a couple of minutes, the police chasing the thief were out of sight from the highway.
- The coach is coaching continuously the same move to their students.
Appositive Phrase:
An Appositive phrase is a better option to provide any additional data in any sentence.
It is a phrase that changes the name of a noun or a pronoun and defines it in another way.
This phrase contains one or more than one word in it.
Examples:
- My favorite bike, Harley Davidson, has an awesome sound.
- Here, “my favorite bike” is an Appositive phrase that gives additive details of the bike of the speaker/subject.
- He owned a supercar car, an Austin Martin, which is very costly.
- Our major project, a renewable energy resource machine, has successfully registered.
- My girlfriend, the soulmate of my life, is going to be my wife very soon.
- His grandfather, Sir Don Bradman, is a well-known industrialist in Asia.
Absolute Phrase:
An absolute phrase is a phrase where the subject is present, but there is an absence of the verb, and hence this phrase is not stand alone.
An absolute phrase contains a subject and a modifier (most probably a participle), but the absence of a verb in it.
An absolute phrase is very difficult to recognize from any sentence.
Sometimes, it requires adding conjunction and rebuilding the participle to the finite verb.
Examples:
- The bike slipped down, most of the people frightened away.
- Here, “the bike slipping down” is an absolute phrase.
- The race finished, my friend came first.
- Let us enjoy the movie. The movie started finally.
- Each student, their faces relieved, and looking happy, enjoyed after the exams.
- The book inside the bag, he reached in the library.