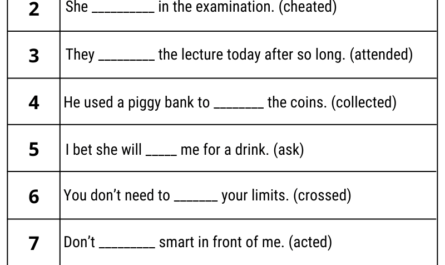
Regular Verb is one of the forms of verbs that are combined in the prescribed format. The verb forms of a regular verb, such as past simple and past participle form, look the same, which has an end or suffix like “-d or -ed” respectively.
Difference between regular verb (Vr) and an irregular verb(Vir)
- Vr- the regular verb expresses the verb in excellent rule to make past simple and past participle forms of the verb.
- Vir- the irregular verb has a different way of end in other forms like in past simple and [ast participle form.
- Vr- it is followed by the pattern of equal modulation of words.
- Vir- it does not follow any similar modulation pattern.
- Vr- the words in regular verbs formation, has many similarities in word, only the end has changed with -d and -ed, called as a verbal end.
- Vir- the word in irregular verbs, completely changed in the past simple and past participle.
For example,
Some rules for regular verbs:
(Work-worked-worked), (stop-stopped-stopped), (laugh-laughed-laughed), etc.
- Usually, add “-ed” at the end,
| Base Form | Past Simple | Past Participle |
|---|---|---|
| accept | accepted | accepted |
| join | joined | joined |
| end | ended | ended |
2. Usually, add “-d” at the end, if the verb ends with the letter “e.”
| Base Form | Past Simple | Past Participle |
|---|---|---|
| love | loved | loved |
| underline | underlined | underlined |
| die | died | died |
3. For a verb that has a consonant end, then double the consonant letter and add “-ed” at the end
| Base Form | Past Simple | Past Participle |
|---|---|---|
| rub | rubbed | rubbed |
| grab | grabbed | grabbed |
| stop | stopped | stopped |
4. For a verb whose last speech sound is stressed and ends, then double the last consonant and add “-ed” at the end.
| Base Form | Past Simple | Past Participle |
|---|---|---|
| prefer | preferred | preferred |
| incur | incurred | incurred |
| rip | ripped | ripped |
5. If the last consonant is “w, x, y,” it will not be doubled.
| Base Form | Past Simple | Past Participle |
|---|---|---|
| play | played | played |
| fix | fixed | fixed |
| review | reviewed | reviewed |
6. For a verb whose first speech sound is stressed and ends, then double the last consonant and add “-ed” at the end.
| Base Form | Past Simple | Past Participle |
|---|---|---|
| open | opened | opened |
| swallow | swallowed | swallowed |
| enter | entered | enteed |
7. If the verb ends with the consonant “y,” substitute “y with i” and add ed at the end.
| Base Form | Past Simple | Past Participle |
|---|---|---|
| try | tried | tried |
| cry | cried | cried |
| fry | fired | fried |
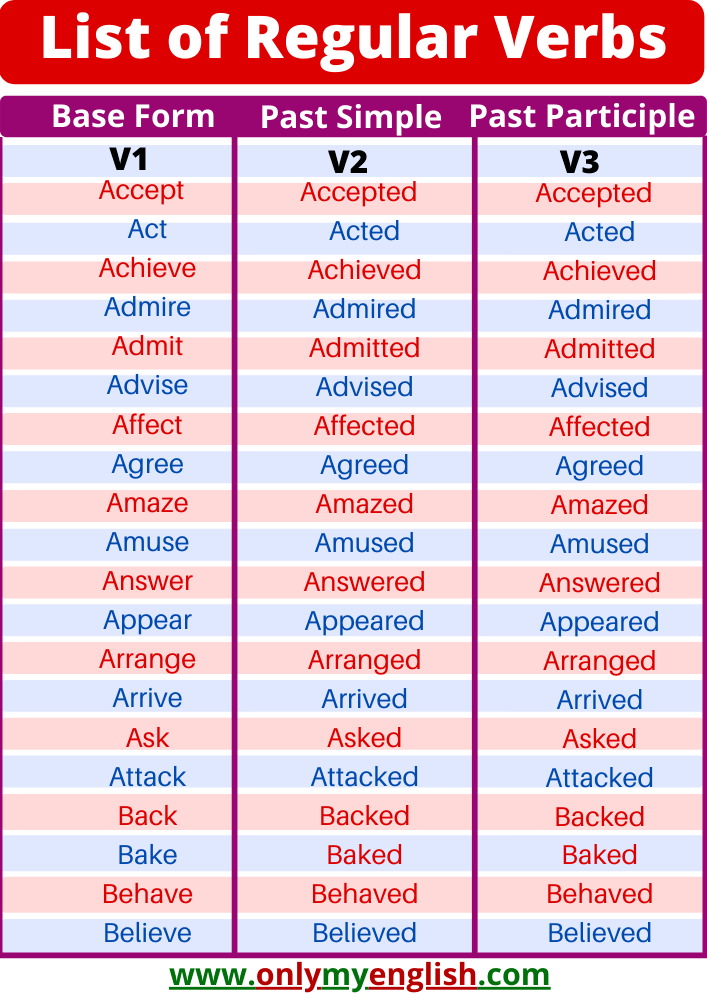
List of Regular Verb
| Base Form (V1) | Past Simple (V2) | Past Participle (V3) |
|---|---|---|
| Accept | Accepted | Accepted |
| Act | Acted | Acted |
| Achieve | Achieved | Achieved |
| Admire | Admired | Admired |
| Admit | Admitted | Admitted |
| Advise | Advised | Advised |
| Affect | Affected | Affected |
| Agree | Agreed | Agreed |
| Amaze | Amazed | Amazed |
| Amuse | Amused | Amused |
| Answer | Answered | Answered |
| Appear | Appeared | Appeared |
| Arrange | Arranged | Arranged |
| Arrive | Arrived | Arrived |
| Ask | Asked | Asked |
| Attack | Attacked | Attacked |
| Back | Backed | Backed |
| Bake | Baked | Baked |
| Behave | Behaved | Behaved |
| Believe | Believed | Believed |
| Belong | Belonged | Belonged |
| Blame | Blamed | Blamed |
| Borrow | Borrowed | Borrowed |
| Bother | Bothered | Bothered |
| Calculate | Calculated | Calculated |
| Call | Called | Called |
| Cancel | Canceled | Canceled |
| Carry | Carried | Carried |
| Cause | Caused | Caused |
| Celebrate | Celebrated | Celebrated |
| Clean | Cleaned | Cleaned |
| Clear | Cleared | Cleared |
| Climb | Climbed | Climbed |
| Close | Closed | Closed |
| Compare | Compared | Compared |
| Compete | Competed | Competed |
| Complete | Completed | Completed |
| Contain | Contained | Contained |
| Continue | Continued | Continued |
| Cook | Cooked | Cooked |
| Correct | Corrected | Corrected |
| Cough | Coughed | Coughed |
| Count | Counted | Counted |
| Crash | Crashed | Crashed |
| Create | Created | Created |
| Cross | Crossed | Crossed |
| Curse | Cursed | Cursed |
| Change | Changed | Changed |
| Chase | Chased | Chased |
| Chat | Chatted | Chatted |
| Check | Checked | Checked |
| Dam | Damed | Damed |
| Damage | Damaged | Damaged |
| Dance | Danced | Danced |
| Date | Dated | Dated |
| Decide | Decided | Decided |
| Deliver | Delivered | Delivered |
| Depend | Depended | Depended |
| Describe | Described | Described |
| Design | Designed | Designed |
| Destroy | Destroyed | Destroyed |
| Dicrease | Dicreased | Dicreased |
| Die | Died | Died |
| Disagree | Disagreed | Disagreed |
| Discover | Discovered | Discovered |
| Discuss | Discussed | Discussed |
| Disturb | Disturbed | Disturbed |
| Dress | Dressed | Dressed |
| Dry | Dried | Dried |
| Earn | Earned | Earned |
| Eliminate | Eliminated | Eliminated |
| End | Ended | Ended |
| Enjoy | Enjoyed | Enjoyed |
| Entertain | Entertained | Entertained |
| Excuse | Excused | Excused |
| Exercise | Exercised | Exercised |
| Exhibit | Exhibited | Exhibited |
| Expect | Expected | Expected |
| Express | Expressed | Expressed |
F to N
| Face | Faced | Faced |
| Film | Filmed | Filmed |
| Fill | Filled | Filled |
| Fish | Fished | Fished |
| Fix | Fixed | Fixed |
| Follow | Followed | Followed |
| Freeze | Freezed | Freezed |
| Fry | Fried | Fried |
| Greet | Greeted | Greeted |
| Guess | Guessed | Guessed |
| Hail | Hailed | Hailed |
| Handle | Handled | Handled |
| Happen | Happened | Happened |
| Hate | Hated | Hated |
| Help | Helped | Helped |
| Hope | Hoped | Hoped |
| Hunt | Hunted | Hunted |
| Identify | Identified | Identified |
| Ignore | Ignored | Ignored |
| Imagine | Imagined | Imagined |
| Impress | Impressed | Impressed |
| Improve | Improved | Improved |
| Include | Included | Included |
| Increase | Increased | Increased |
| Interview | Interviewed | Interviewed |
| Introduce | Introduced | Introduced |
| Invite | Invited | Invited |
| Jog | Jogged | Jogged |
| Join | Joined | Joined |
| Jump | Jumped | Jumped |
| Knock | Knocked | Knocked |
| Label | Labeled | Labeled |
| Land | Landed | Landed |
| Last | Lasted | Lasted |
| Learn | Learned | Learned |
| Like | Liked | Liked |
| Link | Linked | Linked |
| List | Listed | Listed |
| Listen | Listened | Listened |
| Live | Lived | Lived |
| Locate | Located | Located |
| Look | Looked | Looked |
| Love | Loved | Loved |
| Man | Maned | Maned |
| Manage | Managed | Managed |
| Mark | Marked | Marked |
| Match | Matched | Matched |
| Measure | Measured | Measured |
| Mention | Mentioned | Mentioned |
| Miss | Missed | Missed |
| Move | Moved | Moved |
| Name | Named | Named |
| Need | Needed | Needed |
| Note | Noted | Noted |
| Notice | Noticed | Noticed |
| Number | Numbered | Numbered |
O To L
| Offer | Offered | Offered |
| Open | Opened | Opened |
| Order | Ordered | Ordered |
| Organize | Organized | Organized |
| Pack | Packed | Packed |
| Paint | Painted | Painted |
| Paddle | Paddled | Paddled |
| Pamper | Pampered | Pampered |
| Pardon | Pardoned | Pardoned |
| Park | Parked | Parked |
| Participate | Participated | Participated |
| Pass | Passed | Passed |
| Perform | Performed | Performed |
| Persuade | Persuaded | Persuaded |
| Pick | Picked | Picked |
| Plan | Planned | Planned |
| Play | Played | Played |
| Please | Pleased | Pleased |
| Practice | Practiced | Practiced |
| Predict | Predicted | Predicted |
| Prefer | Preferred | Preferred |
| Present | Presented | Presented |
| Program | Programmed | Programmed |
| Protect | Protected | Protected |
| Provide | Provided | Provided |
| Purchase | Purchased | Purchased |
| Push | Pushed | Pushed |
| Race | Raced | Raced |
| Rain | Rain | Rain |
| Receive | Received | Received |
| Recommend | Recommended | Recommended |
| Relate | Related | Related |
| Relax | Relaxed | Relaxed |
| Release | Released | Released |
| Remember | Remembered | Remembered |
| Repair | Repaired | Repaired |
| Repeat | Repeated | Repeated |
| Resist | Resisted | Resisted |
| Rest | Rested | Rested |
| Return | Returned | Returned |
| Review | Reviewed | Reviewed |
| Sail | Sailed | Sailed |
| Save | Saved | Saved |
| Scan | Scanned | Scanned |
| Scare | Scared | Scared |
| Share | Shared | Shared |
| Shop | Shopped | Shopped |
| Shout | Shouted | Shouted |
| Skate | Skated | Skated |
| Ski | Skied | Skied |
| Slow | Slowed | Slowed |
| Sneeze | Sneezed | Sneezed |
| Snow | Snowed | Snowed |
| Solve | Solved | Solved |
| Spell | Spelled | Spelled |
| Start | Started | Started |
| Step | Stepped | Stepped |
| Stop | Stopped | Stopped |
| Stress | Stressed | Stressed |
| Study | Studied | Studied |
| Substitute | Substituted | Substituted |
| Suggest | Suggested | Suggested |
| Surprise | Surprised | Surprised |
| Talk | Talked | Talked |
| Taste | Tasted | Tasted |
| Terrorize | Terrorized | Terrorized |
| Thank | Thanked | Thanked |
| Touch | Touched | Touched |
| Travel | Traveled | Traveled |
| Try | Tried | Tried |
| Tune | Tuned | Tuned |
| Turn | Turned | Turned |
| Underline | Underlined | Underlined |
| Use | Used | Used |
| Vary | Varied | Varied |
| Wait | Waited | Waited |
| Walk | Walked | Walked |
| Want | Wanted | Wanted |
| Warn | Warned | Warned |
| Wash | Washed | Washed |
| Watch | Watched | Watched |
| Water | Watered | Watered |
| Welcome | Welcomed | Welcomed |
| Wish | Wished | Wished |
| Witness | Witnessed | Witnessed |
| Work | Worked | Worked |
| Worry | Worried | Worried |
| Wrestle | Wrestled | Wrestled |
How many regular verbs are there in the English language?
In the English language, there are more than 11,000 regular verbs, excluding the pronominal verbs. This is researched by the RAE (Research Assessment Exercise).
If we include phrasal verbs too along with the verbs, then the number of verbs can rise more than 20,000, respectively.
Basic five-sentence structures for using verbs (regular as well as irregular verbs):
The verbs that explain itself in a sentence are intransitive verbs.
Structure 1:
Subject + verb.
Intransitive verbs do not need any object or any balance to support in a sentence.
- He slept.
- They played.
Structure 2:
Subject + verb + object.
It involves a supportive object to which a transitive verb depends on. But in this structure, the object does not give a full modification about the subject. It only implies to help the verb.
- He ate breakfast.
- She fell down.
Structure 3:
Subject + verb + subject complement (as object)
The verb that is used is called a linking verb, where an object complements the subject and is combined in a sentence with the linking verb’s help.
Here, the linking verbs are not regular verbs; it should be in “to be” form.
- He is a brave person.
- She is intelligent.
Structure 4:
Subject + verb + indirect object +direct object.
This structured sentence contains two objects, direct and indirect. It gives all the information related to the subject and the verb, respectively.
- He fell to the ground.
- She smiled in the middle of class.
Structure 5:
Subject + verb + direct object + complement noun object.
- He fell due to the mud on the ground.
- She smiled at her friend in the middle of class.
Examples of Regular Verbs are in Sentences
- My brother loves your sister for so long.
- All dresses have dried very quickly in this hot climate.
- Suddenly, he turned his car to take a highway route.
- I don’t know why he behaved like a kid at the party?
- She slowed down her vehicle when she crossed the bridge.