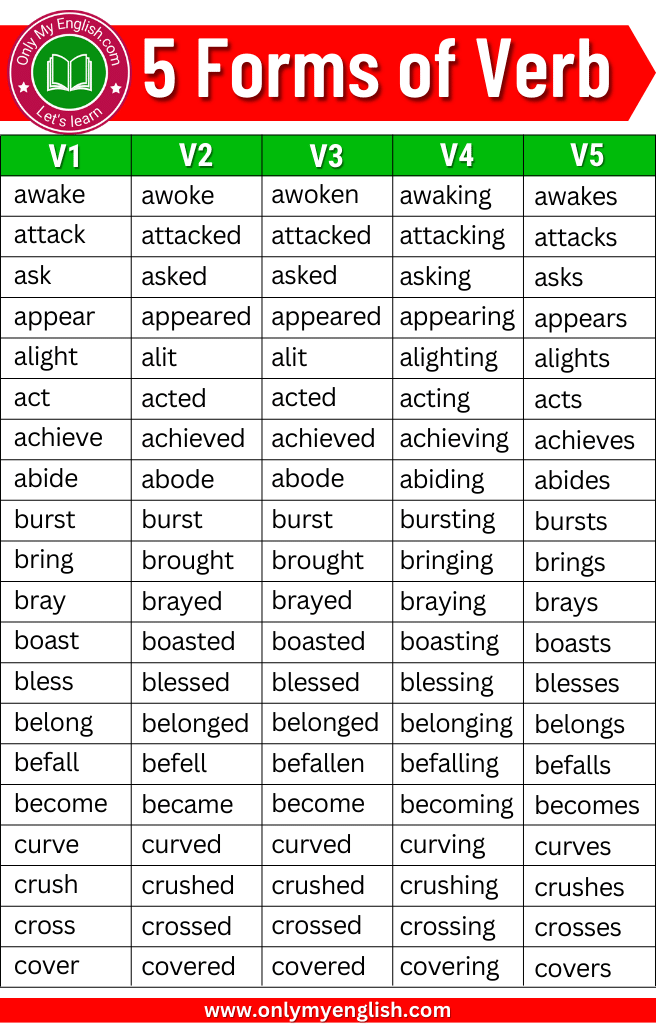
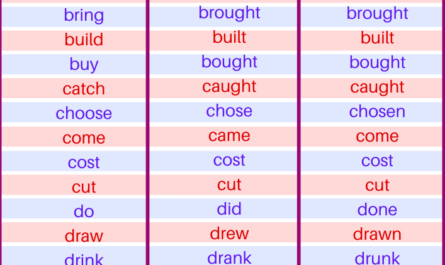
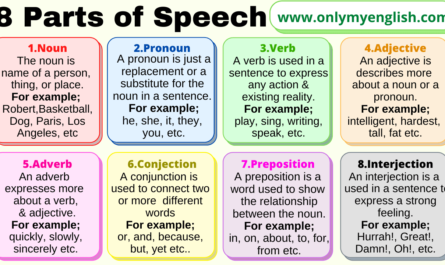
Definition:
A-verbs is a word or a group of words used in a sentence to exhibit an action, existence, and occurrence. It is responsible for the performance of the subject in a sentence according to the tense. there are nine different types of verb.

There are eight different types of verb:
- Finite verbs
- Non-finite verbs
- Stative verbs
- Action verbs
- Transitive verbs
- Intransitive verbs
- Linking verbs
- Modal verbs
- Auxiliary verbs
1. Finite verbs:
Finite verbs are also called the limited verbs, or the actual verbs are the background of sentences. According to the number or person of the subject in a sentence, a finite verb can be used from one of the twelve tense forms.
Examples of finite verb are in sentences
- John forgot his briefcase at home.
- She is dancing on the stage.
- This team is one of the best teams performed in the Olympics.
- He is driving continuously for a couple of hours.
- The dog smells a bone placed in the garbage.
2. Non-finite verbs:
Non-finite verbs are opposite to the finite verbs, which is not actual. It works as a noun, adjective, adverb, etc. in a sentence despite working as a verb. It does not change according to the number or person of a subject; sometimes, it functions as a subject.
Gerund, infinitive, and participle (participles turn finite verbs if added auxiliary verbs) are the forms of non-finite verbs.
Examples of non-finite verbs are in sentences
- Sam woke early and went to the gym. (infinitives)
- Listening helps to increase knowledge. (Gerund)
- Working on farmland makes you active. (Present participle)
- The nail is twisted by hammering. (Past participle)
3. Stative verbs:
Stative verbs are ultra-fine, and it is quite complicated to judge verbs. They express any existence (state of being in mental, physical, and emotional means) or any position, which has no time span, neither starting nor an ending point; also, no action takes place.
There are four types of stative verbs explained by the help of examples,
- Qualities / Being verbs
- Sensing verbs
- Emotional verbs and
- Possession verbs.
a) Qualities / Being verbs:
The verbs that indicate any quality or state of being, regarding the subject in a sentence is called qualities/ being verbs.
- Consist, involve, contain, attain, require, be, have, etc.
b) Sensing verbs:
Sensing verbs express some sense or feel in a sentence.
- The smell, hear, taste, touch, look, sound, etc.
c) Emotional verbs:
Emotional verbs express certain emotions or feelings of a person.
- Forget, remember, think, enjoy, believe, love, doubt, understand, etc.
d) Possession/controlling verbs:
Possession verbs are also meant to own something or be in control of.
- Live, belong, own, stand, face, etc.
Examples,
- Remo loves swimming in the river.
- You should respect your elders; they deserve it.
- That recipe smells so delicious.
- I have a better idea to go out of this forest.
- My dad owns this property after my grandfather’s death.
4. Action verbs:
A verb is called an action verb when it shows any action or performance of the subject (a person or a thing) in a sentence. It is also called a dynamic verb.
- Sleep, run, eat, drive, listen, carry, read, throw, play, etc.
Action verbs can also be transitive or intransitive.
Examples of action verbs are in sentences
- Sunny is adopting a baby from an orphanage.
- She is cooking food for his younger brother.
- He is anchoring on the stage in today’s event.
- She always listens to her parents.
- The truck carries a massive load from its capacity.
5. Transitive verbs:
Transitive verbs need a direct object in a sentence on which an action is taking place.
Examples of transitive verbs are in sentences
- He drove the plane in an emergency.
- He ate his dinner before the time.
- She baked a cake for her friend’s birthday.
- I delivered the consignment.
- My father took me to the hospital when I was sick.
6. Intransitive verbs:
Intransitive verbs do not need a direct object in a sentence. It may be acted with an adverb, preposition, adjective, noun, and other parts of speech present in a sentence.
Example of intransitive verbs are in sentences
- After his accident, Gorgie unable to read or write.
- Suddenly he laughed.
- It’s snowing.
- Something has happened.
- He sleeps at night.
Note: A subject and an intransitive verb together can make a sentence.
7. Linking verbs:
The linking types of verb shows a link between a subject and the object in a sentence. It does not show any action in a sentence. ‘Am, is, are’ are called as be verbs in a linking verb.
Although linking verbs are
- Grow, feel, taste, remain, appear, act, smell, sound, become, stay, etc.
Examples of linking verbs are in sentences
- This store remains open the whole night.
- They all are going to excavate.
- The smell of the soil is awesome in the rainy season.
- I am Jayson Fernandezz.
- The rainbow appears in the sky after the rain.
Still, linking verbs are of two types,
- True linking verbs and
- Linking/action verbs.
a) True linking verbs:
- Am, is, are, has, was, were, become, being, seems, etc.
Examples,
- He was jealous.
- They are ready to fight.
- The roller coaster is moving faster.
b) Linking Verbs or Action Verbs:
- Remain, stay, turn, grow, feel, prove, get, etc.
Examples,
- She disappears after the party.
- She frequently looked at me.
- The fresh vegetables smell good.
8. Modal verbs:
A modal verb is used to help the main verb to show expectation, ability, potential, way of possibility, etc. A modal verb is moderately an auxiliary verb.
All modal verbs are auxiliary verbs, but all auxiliary verbs are not modal verbs.
examples: Must, can, could, may, should, might, would, will, shall, etc.
Examples modal verbs are in sentences
- You must go to the gym.
- They should follow the rules of the match.
- She will reach there at any time.
- I would not allow you to finish all the pizza slices.
- It might be an accidental meeting, but we met by destiny.
9. Auxiliary verbs:
Auxiliary types of verb are also called helping verbs. It helps the main verb to extend its meaning in a sentence.
examples: Is, am, are, was, were, have, has, shall, will, etc.
Examples of auxiliary verbs are used in sentences
- He is coming from London by flight.
- They are performing well in tournaments.
- He has not completed his homework.
- I will go to practice hockey.
- We are shifting to Poland after a few days.